Last Reviewed and Updated on February 21, 2023
Axolotls are amongst the most unique salamanders, as unlike many others, they remain aquatic throughout their lives. But they are still amphibians, so the question is can axolotls breathe air in their adult stage like most other amphibians do? Let’s find out.

What are axolotls?
Axolotls are a type of salamander, specifically a neotenic salamander. Neoteny is a condition where an organism reaches sexual maturity without undergoing metamorphosis.
Salamanders, axolotls included, are amphibians. Most salamanders have a life cycle that starts in water; they lay eggs in the water. Larvae hatch and live in the water; they breathe air through their gills. These gills are lost in most species when they undergo a metamorphosis. As they undergo the metamorphosis, they develop eyelids, tongues, and teeth and move to the land where they use their lungs for breathing. While this is true for most salamanders, not all salamanders have the same reproduction cycles and life cycles, and many are pretty complex and may even vary within the same species (source; Variation in the Life Cycle of the Salamander Gyrinophilus porphyriticus by R.C. Bruce).
Axolotls are among rare salamander species that retain their larval features throughout their lives and almost never undergo full metamorphosis. Unlike most salamanders that live on land (near water) after the metamorphosis, almost all axolotls remain aquatic throughout their lives.
Fun fact: even though axolotls generally don’t generally undergo metamorphosis, they can under certain conditions. Want to learn more? Read this list of interesting axolotl facts.
Can Axolotls Breathe Air From the Surface?
So since axolotls do not undergo metamorphosis and stay aquatic, do they still have the means (lungs) to breathe air?
The answer is yes; they can breathe air in addition to extracting oxygen from water. Axolotls, however, won’t do well by breathing through their lungs alone, as while functional, the lungs are underdeveloped. Axolotls primarily breathe through their gills, so breathing through the lungs alone would lead to oxygen deprivation.
These animals possess underdeveloped but functional lungs similar to other air-breathing animals and can use them to supplement their oxygen supply in times of low oxygen levels in the water or when they are out of water for a short period of time (study Surfactant proteins and cell markers in the respiratory epithelium of the amphibian, Ambystoma mexicanum).
It is crucial to remember axolotls, with the exception of a few that undergo metamorphosis, are aquatic animals, and even though they can breathe air from the surface, they won’t survive out of water for a longer period.
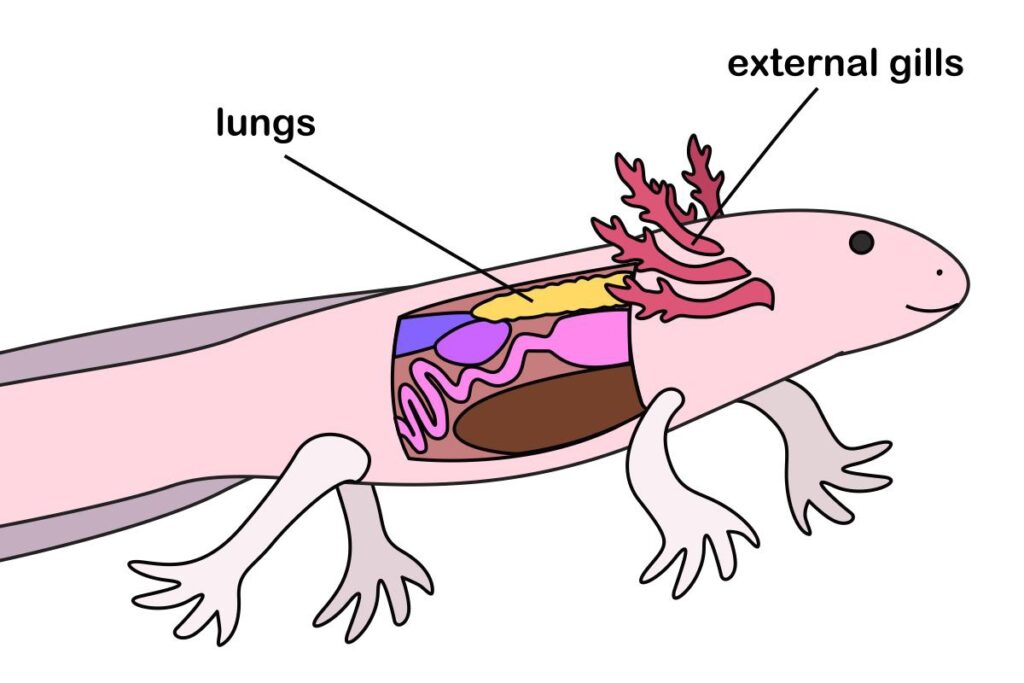
In addition to gills and lungs, axolotls also exchange gas through their skin.
What happens if they undergo metamorphosis?
Typically an axolotl won’t undergo metamorphosis naturally, but this can occur occasionally. The metamorphosis can also be artificially induced. If they undergo the metamorphosis, they will lose their gills and won’t be able to breathe underwater anymore. They will breathe air primarily through their lungs like most other salamanders.

Because these amphibians are rather unique, it comes as no surprise they got their spot on our list of most unique animals in the world. Want to learn who the other 99 animals are? You are going to love this list.
Explore this list of the 100 strangest animals in the world.
