Last Reviewed and Updated on March 11, 2023
The gulper eel, with a distinctive appearance and unusual behavior, is one of the most unique eels in the world. Let’s dive deep into the abyss and explore some fascinating facts about the gulper eel, from their large mouths to bulb-like noses.
About Gulper Eels
Gulper eels (Eurypharynx pelecanoides), also known as pelican eels, umbrella-mouth gulper, or pelican gulper, is a deep-sea eel belonging to the genus Eurypharynx. They are found in all of the world’s oceans in temperate and tropical waters. Gulper eels seem to be living at depths between 1,600 to 9,800 ft / 500 to 3,000 m.
There is only one confirmed species of gulper eel, they were once placed in order of their own but are now considered true eels.
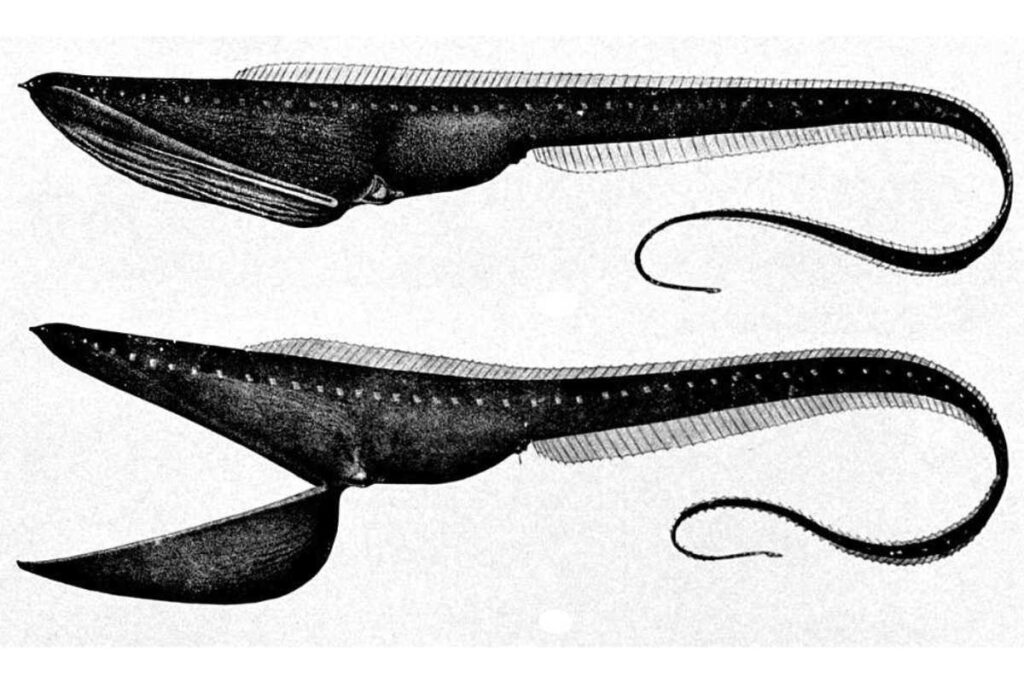
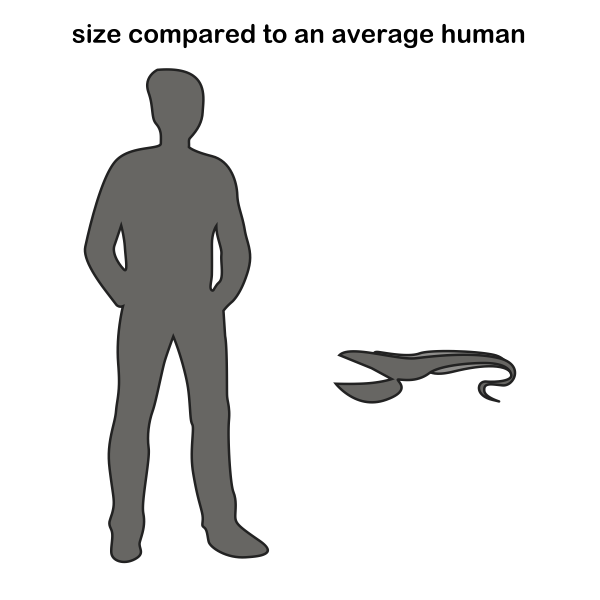
As their bodies are adapted to living in the deep sea, they are very fragile when caught and lose their shape. The gulper eel was first directly observed in its habitat only in 2018. Gulper eels have a distinctive appearance, with an elongated body that is about 2.5 feet / 75 cm in length, but it’s presumed they grow to 3 feet / 1 meter in length. They have large mouths, measuring about a quarter or a thrid of their total length. They can open and expand their mouths wide, giving them their nickname “pelican eels.” Their bodies are generally black or dark olive, and they have small eyes.
Gulper eels feed on a variety of deep-sea creatures, including squid, crustaceans, and other fish. Their favorite? Small crustaceans.
We do not know much about their reproduction. Like other eels, females likely release eggs into the water, which males fertilize. The larvae that hatch from the eggs are pelagic and drift with the currents before settling to the seafloor as juveniles.
The conservation status of gulper eels is listed as “least concern” by the IUCN.
Gulper Eel (Eurypharynx pelecanoides)
Size: about 2.5 ft / 0.75 m
Weight: unknown
Color: black or dark olive
Lifespan: unknown
Habitat: deep sea
Interesting Facts About Gulper Eels
Ready for some mind-blowing facts about gulper eels?

Love unusual creatures? Check out our list of the weirdest animals ever.
1. Their mouth is much larger than their body
The mouth of gulper eels is about a quarter, or even close to a third of their total length, tail included. Their head, with their mouth, is much larger than the body (abdomen part, without tail) of this peculiar eel species.
2. They can open their mouths wide enough to swallow prey larger than they are
Wondering how wide can a gulper eel open its mouth? They have an incredibly large mouth that can open wide to swallow prey much larger than they themselves are.
The jaw is loosely hinged and can be extended to accommodate large prey. In addition to that, their stomach can stretch and expand to accommodate large meals.
3. Gulper eels don’t have a swim bladder
Gulper eels do not have swim bladders like most fish do. A swim bladder is an internal gas-filled organ found in many fish that helps them control their buoyancy and maintain their position in the water column.
So how do gulper eels control their buoyancy? The “lymphatic spaces” located around vertebrates of pelican eels are filled with a gelatinous substance that is thought to function in a similar way as the swim bladder does. Aglomerular kidney maintains this jelly-like substance (source).
4. For deep-sea fish, the Gulper eels have very small eyes
Deep sea animals often have larger eyes relative to their body size compared to shallow-water animals. This may be because the deep sea is a very dark environment where very little sunlight penetrates, and in order to see, deep-sea animals have evolved larger eyes to capture as much light as possible to form images.
Gulper eels have very small eyes; the reason behind this is believed to be that this species evolved in a way to detect faint traces of light with their eyes rather than see images.
5. Gulper eels are bioluminescent
Bioluminescence is the ability of organisms to produce light. Many deep-sea creatures, including gulper eels, use bioluminescence to communicate as well as attract prey in the dark ocean depths.
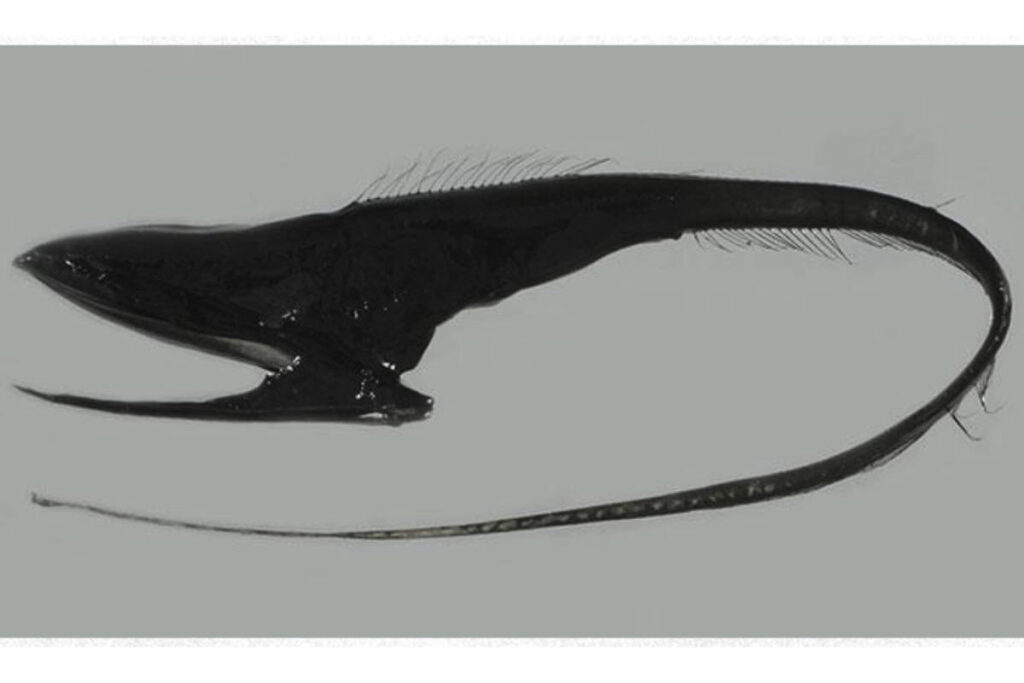
Gulper eels have bioluminescent organs called photophores on their tail. These photophores produce light through a chemical reaction.
6. The tip of their tail glows pink
The most common color in deep sea creatures is blue-green. Red is also fairly common. The tip of the gulper eel’s tail has a complex organ with tentacles that glows pink! How cool is that? It also occasionally emits bright red flashes.
It is thought this serves as a lure for their prey, although the location of this lure is rather unusual, and if this is indeed the case, then this eel needs to assume some weird postures when it hunts.
7. Pelican eels actively hunt their prey
Deep-sea fish have evolved a wide range of feeding strategies that allow them to survive in this low-food environment, from filter feeding and suction feeding to other methods. Studies have shown gulper eels are active hunters that pursue their prey. Gulper eels are probably incapable of suction feeding (source).
8. Gulper eels have tiny teeth
Despite them having large mouths and being predators, these fish have very tiny teeth.
9. They don’t have red blood cells until reaching the juvenile stage
Like other eels, gulper eels lack red blood cells during their larval phase. The larvae are transparent.
10. You can tell the male gulper eel from the female by looking at their nose
Gulper eels display sexual dimorphism, meaning there are visual differences between males and females. The nasal rosette of females is barely noticeable, while males have a large nasal rosette that is bulb-shaped.
